Albany Gastroenterology Consultants Has Joined Allied Digestive Health, a Leading Gastroenterology Provider Network
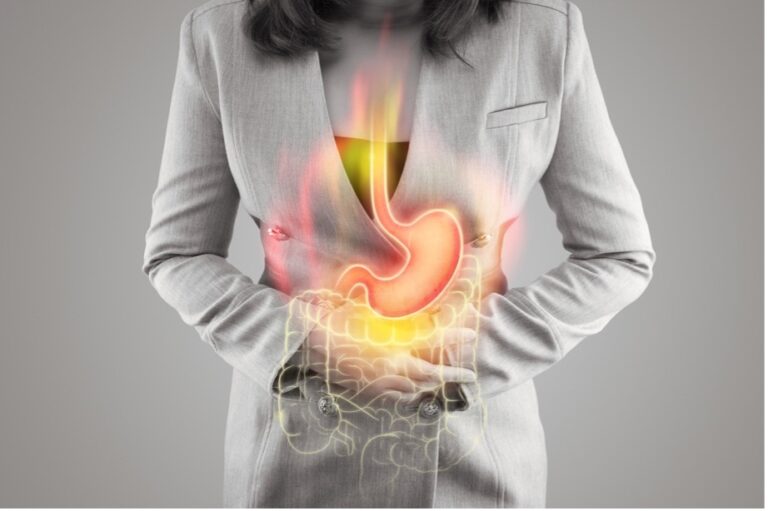
GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) is one of the most commonly diagnosed digestive disorders in the US. It affects 20% of all Americans of all ages, from newborns to older adults. One of the tell-tale signs of GERD is abdominal pain accompanied by the taste of stomach fluid in the back of your throat.
Abdominal pain is a symptom of many problems. The discomfort can be caused by an infection, constipation, a kidney stone, appendicitis, or cancer. So how do you know if you have abdominal pain and GERD or something else? Read on as we learn more about abdominal pain and GERD.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a prevalent chronic condition. It occurs when stomach acid regurgitates into the esophagus. This is caused by a loose lower esophageal sphincter (LES) that allows stomach acid to flow back up the throat. As this happens, there’s inflammation and irritation of the lining of the esophagus, and one may experience abdominal pain, which varies in severity and location.
The pain ranges from a dull ache to a sharp or burning sensation. The pain is often felt in the mid-chest or upper middle of your abdomen (or epigastric region). Some people with abdominal pain and GERD may experience this discomfort after eating spicy foods, fatty meals, or drinking alcohol.
GERD is classified into three types:
The symptoms are almost similar in each type. The main difference is the severity of symptoms which is dictated by several factors, including:
In addition to abdominal pain, the most common symptoms of GERD include the following:
The severity of GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) and stomach pain varies from person to person. In some cases, GERD-related stomach pain is mild and occasional but can be more severe and persistent in others, significantly impacting the quality of life.
While GERD-related stomach pain is not typically considered a medical emergency, it can worsen symptoms if ignored. In some cases, GERD can lead to complications such as inflammation, ulcers, bleeding, scarring, and narrowing of the esophagus. If left untreated, one develops the severest type of GERD, Barrett’s esophagus, which puts one at high risk of esophageal cancer.
Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment of GERD-related stomach pain help improve quality of life and reduce morbidity. The goal is to reduce the amount of stomach acid that flows back into the esophagus, relieve symptoms, and prevent complications. GERD-related stomach pain is typically treated with a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and in some cases, surgery.
Specific lifestyle changes help reduce the frequency and severity of GERD symptoms. These include avoiding trigger foods (such as spicy or fatty foods), losing weight, quitting smoking, and avoiding eating large meals in one sitting.
The physician prescribes medications that reduce the amount of acid in the stomach to relieve GERD-related stomach pain. Antacids are known to provide quick relief by neutralizing stomach acid. On the other hand, H2 receptor blockers reduce the amount of acid produced by the stomach, while proton pump inhibitors block the production of stomach acid altogether. Some of these medications are available over the counter.
In some cases, surgery is recommended to treat GERD-related stomach pain. Fundoplication is a surgical procedure that involves wrapping the upper part of the stomach around the lower esophagus to create a tighter barrier between the stomach and esophagus, preventing acid reflux.
There are several things you can do to prevent GERD-related stomach pain. Here are some tips:
GERD-related is a chronic condition that occurs when stomach acid regurgitates into the esophagus, causing inflammation and irritation of the lining of the esophagus. It is characterized by abdominal pain alongside other common symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, chronic dry cough, difficulty swallowing, nausea, vomiting, and hoarseness. While GERD-related stomach pain isn’t a medical emergency, it can lead to esophageal cancer if left untreated. Treatment includes lifestyle changes, medications, and in some cases, surgery.
If you are experiencing GERD-related stomach pain, seeking treatment from a doctor is crucial. We provide various treatment options for GERD-related stomach pain. Contact us today to identify the best course of treatment that meets your specific needs.
For Your Visit
Albany
P: (518) 533-5000
F: (833) 438-1946
1375 Washington Ave, Suite 101
Albany NY, 12206
Office & Lab: Suite 101
Endoscopy Center: Suite 201
Infusion Center: Suite 101
Mon – Thurs: 7:30 AM – 5:00 PM
Fri: 7:30 AM – 4:00 PM
Sat & Sun: Closed
Clifton Park
P: (518) 533-5000
F: (833) 438-1946
1785 Route 9, Suite 101
Clifton Park, NY 12065
Mon – Thurs: 7:30 AM – 5:00 PM
Fri: 7:30 AM – 4:00 PM
Sat & Sun: Closed
© All Rights Reserved